the open way

Catenda, modern BIM collaboration
Collaborate with subcontractors, coordinate models, detect clashes, and track design changes.
Get everyone up to speed in no time, in an intuitive platform that works seamlessly with your existing tools.

Used and loved by
Catenda Hub
Single point of truth: Eliminate version chaos and streamline collaboration, by having all information in one platform.
BIM Models
Issue Tracking
Handle documents in the context of the design you’re working on.
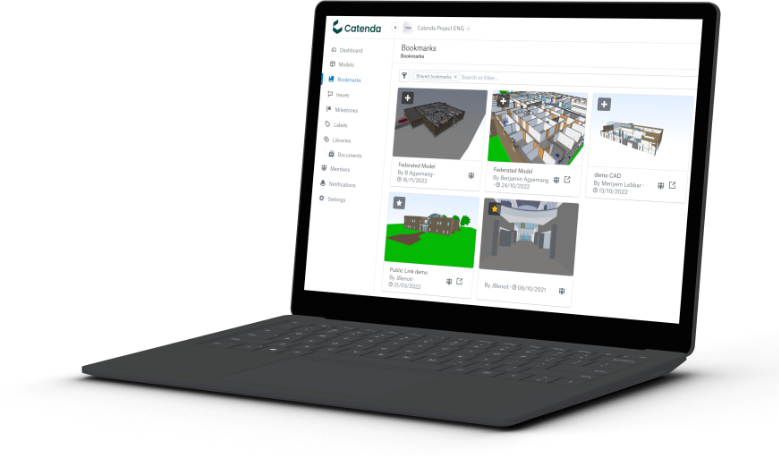
Catenda Site
Bridge the office-site gap with our mobile BIM solution. Access your projects anywhere, anytime.
Documents
Read drawings, directly on your phone.
Issues
Take pictures, create and assign issues.
Offline ready
Work on projects, even when you don’t have internet.
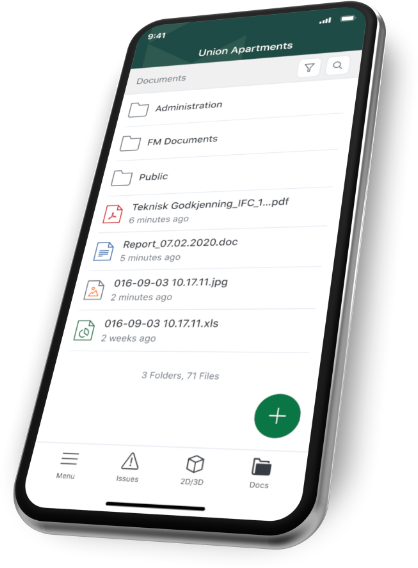
Catenda Duo
Leverage your BIM data for more efficient building operations.
Smart Facility Management
Allocate buildings’ resources effectively for sustainable operations.
Energy Optimization
Maintain your buildings in an energy efficient way with the installed sensors.
B.M.S & IoT
Analyze cloud-stored sensor data for informed decision-making.
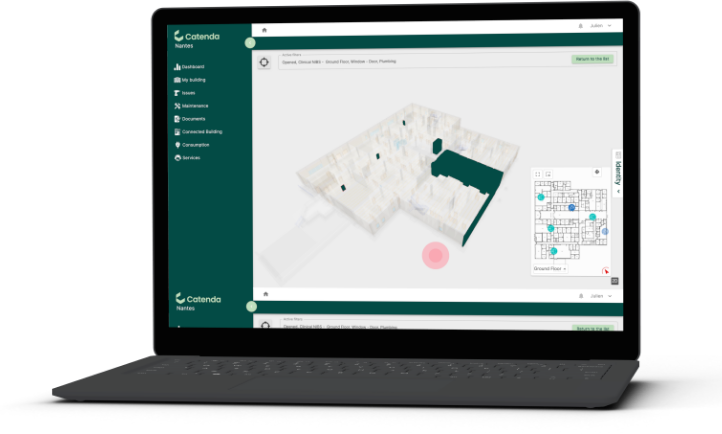
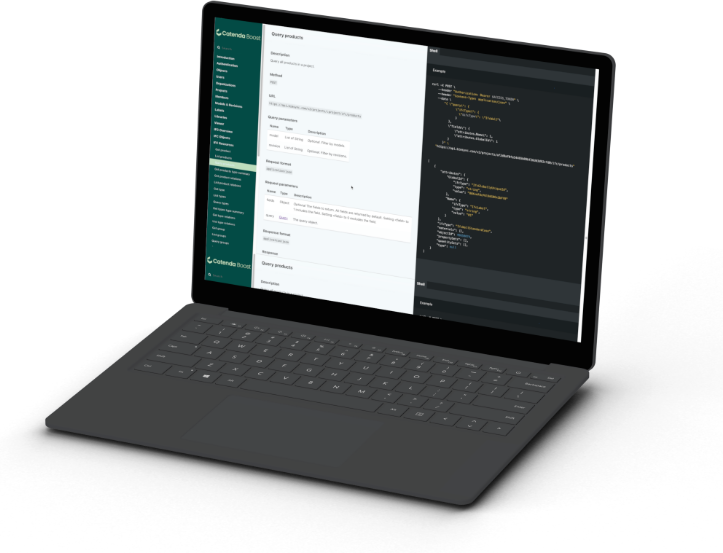
Catenda Boost
Seamlessly integrate Catenda with your existing tools or build innovative solutions using our robust API.
Advanced Viewer Technology
Easily read and write BIM data with our 2D and 3D visualization APIs.
Open CDE Standards
Ensure seamless communication and data exchange across different platforms with standard open CDE APIs.
See why they love Catenda
Our
news
The latest updates from Catenda, news from the world of BIM and open data.

FAQs
What is Catenda Hub used for?
Catenda Hub can be used to centralize all your project data in one place. You no longer need to manually track down email attachments or check version histories. Everything is accessible and updated in real-time, significantly reducing administrative tasks. With Catenda Hub, you can aslo identify issues and clashes in real-time before meetings, allowing you to focus on solutions rather than problem-spotting.
Does Catenda Hub work with our existing tools?
Absolutely. Catenda Hub is designed to integrate seamlessly with a wide range of popular BIM authoring and analysis tools such as Revit, Naviswork, Solibri, MS Teams, etc. It acts as a central hub, connecting your existing toolset without requiring a complete overhaul of your workflow.
How does Catenda Hub facilitate collaboration with external subcontractors?
Catenda Hub supports open standards like BCF and IFC, making it easy to collaborate with external parties regardless of their preferred tools. You can easily share models, assign tasks, and track progress with subcontractors all within the platform.
Is Catenda Hub suitable for both building and infrastructure projects?
Yes, Catenda Hub is versatile and can be used for both building and infrastructure projects. Its flexible architecture allows it to handle various project types and scales, making it an ideal solution for diverse BIM management needs.
We are proud to be part of
organizations and
research programs
Since day one, we have worked with international organizations to improve collaboration, openness, efficiency and sustainability in the construction sector.