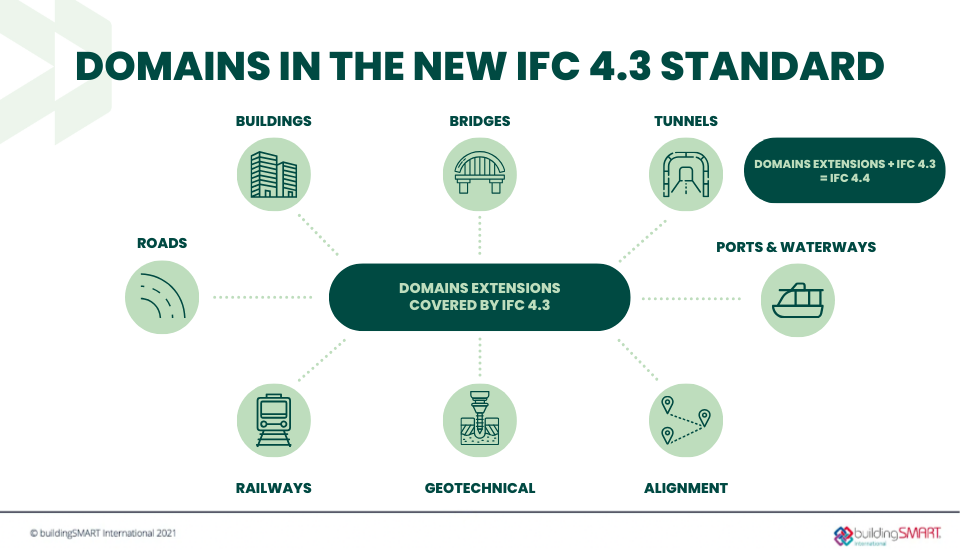
The earth is spherical and its surface is essentially curved. As infrastructure stretches across different terrains, it is significant to introduce an updated IFC to thoroughly support the horizontal assets. The IFC 4.3 is now levelled up to cover the full scope of landscapes, including road, railway, ports and waterways, bridges, and the common elements between all these.
This was a significant step forward for buildingSMART, and it signifies further progress in guaranteeing support for the most current standards for the intended global rollout.
Source: BuildingSMART
What is IFC 4.3 version? An overview on the latest IFC 4.3 schema
IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) is a schema composing multiple layers stacked on top of each other. Ranging from generic layers to particular ones in the hierarchy, IFC 4.3 is a comprehensive version that contributes to the development of openBIM.
1. Resource Layer
This layer is the place where the basic building blocks are stored. It might be said to be extremely broad since these items below can be listed in any other industry, not specifically in the AECOO environment.
For instance, some disciplines can be named as following:
- Units definition
- Shape / geometry / structural object
- Date and time descriptions
- Money and currencies
- Property data types
However, it is not deniable that some elements such as shapes or structural objects are highly typical for the construction and building industry.
2. Core Layer
Although the second layer still represents a generic part of IFC, some academic words and technical language start to emerge. Basic objects, various types of relationships and property sets are the main assets to discuss in this layer.
Despite the basic information they hold, the resource and core layer set a solid digital foundation for the industry to lean on and continue evolving.
3. Shared Layer
Unlike the 2 previous ones, the shared layer is characterized by a set of common things, containing both physical objects and broad entities, in the AECOO industry.
The physical elements can be listed as
- Walls
- Stairs, windows
- Fasteners
- Earthworks
- MEP fittings
The broad things are defined as
- Definitions for management and facilities
- Permits, cost schedules, furniture and occupants.
4. Domain Layer
The domain layer is the most specific one out of 4. In the latest version IFC 4.3, the list of disciplines has been expanded to include many new useful properties.
- Architecture
- Building controls
- Construction management
- Electrical
- HVAC
- Plumbing fire protection
- Ports and waterways
- Rail
- Road
- Structural elements and analysis
Tunnel is not officially mentioned yet because it is still in progress. Once it is set and done, the new IFC promises to bring more genuine values for BIM adoption and implementation. The buildingSMART orgnization is working hard to add more and more disciplines to enrich its neutral platform.
The Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) model is a standardized data model for the exchange of building and infrastructure information. IFC 4.3 is the latest version of the IFC model, and it includes a number of new and updated features specifically designed for the modeling of infrastructure projects.
Some marked improvements in the latest version of IFC 4.3
Support for the horizontal assets
The IFC 4.3 program was established to extend the IFC benefits for horizontal assets. The IFC 4.3 manages quite well several geographical limitations existing in the previous version. The major changes allow a more precise description of infrastructure stretching across a large area along the horizontal axis.
Infrastructure domain extension supported
Infrastructure domain that the new IFC covers is becoming more and more complete, from road, railway to bridge and waterways. This can be considered as a revolutionary enhancement that helps raise the bar in the pathway toward OpenBIM.
Elaboration of definitions and information about the characteristics of infrastructure elements
In the IFC 2×3, the BIM objects are general and contain a poor set of information and data. However, the IFC 4.3 has been upgraded significantly, providing more details and specific information regarding the industry as well as the property and performance of infrastructure elements.
Facilitation of data exchange between different software and systems
No matter what software and system is used, the new IFC supports various formats, namely EXPRESS, STEP, XML, and JSON, ensuring that BIM data can be shared and understood across different software platforms. Furthermore, in the latest version, the IFC documentation can be generated and works well across platforms on Windows, Linux or MacOS.
The new IFC project for horizontal asset extension includes 2 phases. While the first phase focuses on defining the IFC entities for use cases, the second phase has a particular purpose to produce test instructions and deliver software validation of the IFC 4.3 standard.
ISO has accepted the IFC 4.3 submission as a draft international open standard and is progressing it to be published as a new release of ISO 16739 in 2023. At the end of the process, with a rich set of BIM data inside, the IFC 4.3 is expected to be the most comprehensive tool for modeling and exchanging information. Thanks to that, the accuracy, efficiency, and sustainability of the BIM projects can be greatly enhanced in the near future.