As part of an innovation project, COPASA has realized BIMSAFETY-ROADS, with the aim of bringing BIM closer to horizontal construction projects, specifically to road maintenance, focusing on traffic safety management and prevention of work accidents.
The challenge
The road network is the transportation infrastructure that provides society with the greatest mobility (91% of personal trips and 84% of freight trips use this mode of transportation). In order to offer a correct service to citizens through this type of transport, it is essential to develop road conservation, maintenance and operation operations.
As far as safety is concerned, the system is complex. On the one hand, there is road safety, i.e., everything related to traffic accidents. On the other hand, there is risk prevention for the infrastructure maintenance workers themselves. In some cases, these two aspects can be directly linked (traffic accidents affecting maintenance workers in the course of their work). And, in general, they can be linked, directly or indirectly, to the quality of the maintenance service offered to users.
Therefore, in the development of the maintenance and operation of the different sections of the road networks, it is necessary to record, process and manage the information related to these aspects. The organization and analysis of all this information in a practical, fast and flexible way thanks to the new technologies associated with Industry 4.0 could mean, from our point of view, a breakthrough phenomenon in the way to deal with its problems.
How can BIM contribute?
BIM, as a collaborative work methodology for the creation and management of infrastructure, allows the centralization of information in a digital model that can be used by all the stakeholders involved throughout its life cycle. This is fully applicable to the management of road maintenance safety, associated with all the digital tools for the development of the methodology during, in this case, the operation of a road.
The application of these principles on a portion of road or highway focused on the management of road safety and prevention of occupational hazards for operators has great potential. The added value is then the visualization of the accident distribution on the infrastructure model. This facilitates both the quick recognition of the places where they are concentrated and the detailed analysis of the three-dimensional model (such as the signalling, marking and defense elements that are available in the area and all the information collected at the time of the accident). It is also obvious that the possibility of reproducing an incident in a virtual environment allows to analyze its origins and characteristics.
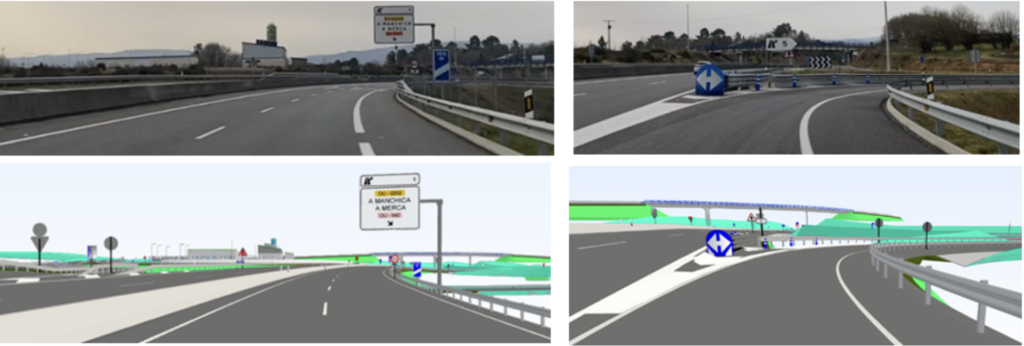
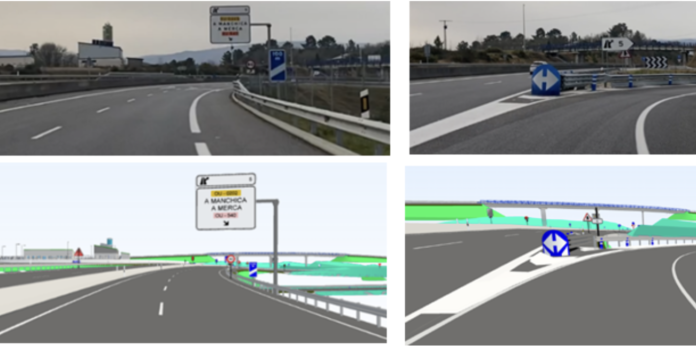
Comparison between images taken "in situ" and images extracted from a 3D road model.
The project
This project developed by COPASA aims to improve security in conservation in a global way. They have combined the power of a platform such as Catenda Hub (previously Bimsync), using BIM methodology, and data processing through artificial intelligence and virtual reality applications. They can take advantage of all these digital technologies for the effective management of road safety, prevention of occupational hazards and quality of service provided to the user in the operations of conservation, maintenance and operation of roads.
The idea is to generate an intelligent information management tool. This tool exploits the potential of both interactive data analysis and three-dimensional visual representation, facilitating safety assessment from multiple angles and in near real time.
IFC models were produced with the road layout, signage and structures of the AG-31 highway.
Data from all issues generated, whether traffic or work related, are collected using Catenda Hub (previously Bimsync) issues boards and their corresponding models.
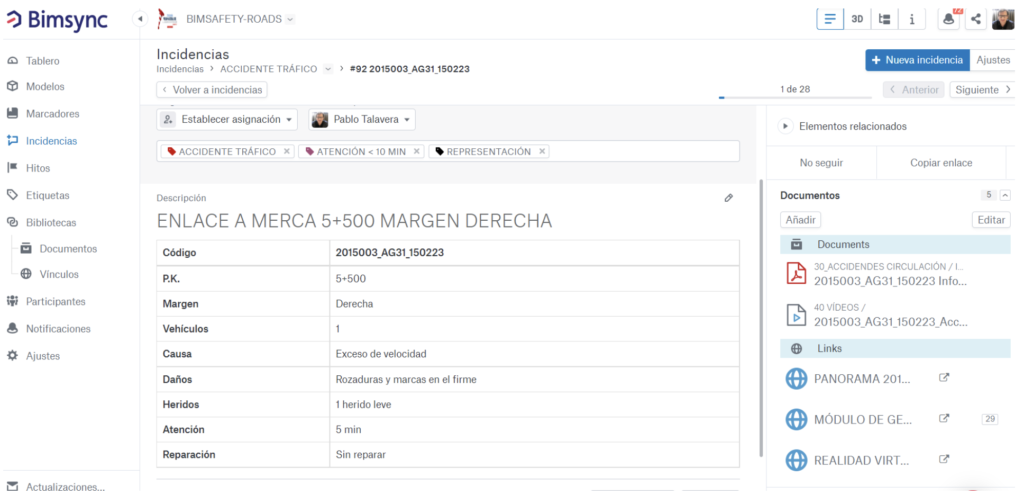
Recorded issues
Together, accident-related documents such as photographs, damage reports or drawings are housed in a folder structure within a Catenda Hub (previously Bimsync) library. All these documents are linked to the corresponding issue.
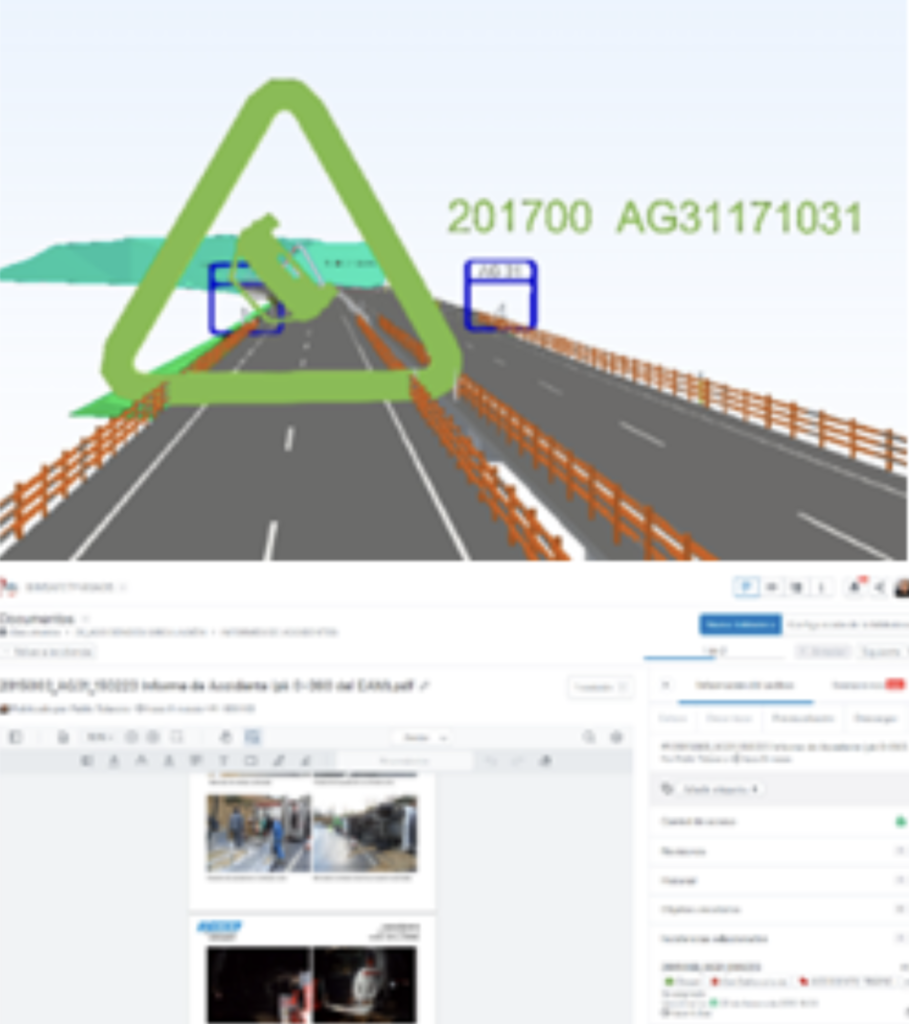
In order to correctly place the accident in space, a large generic object comprising the accident code is modeled. In this way, the information entered in the issue, the documentation and the BIM are linked together.
By generating different labels, issues can be labeled according to the degree of compliance with the service indicators that have been established for each maintenance and retention contract.
Service compliance labels
For a better understanding and analysis of the data generated in each of the incidents, a connection is made between them and other external data such as weather or road condition surveys through a Business Intelligence tool, thanks to Catenda Hub Manager. This allows the configuration of a series of control panels that organize the information so different situation analyses can be performed. It also helps in the decision making process for the implementation of preventive measures to reduce traffic or work incidents, as much as possible.
In addition, a control panel has been created to monitor the degree of compliance with the service indicators included in the maintenance contract.
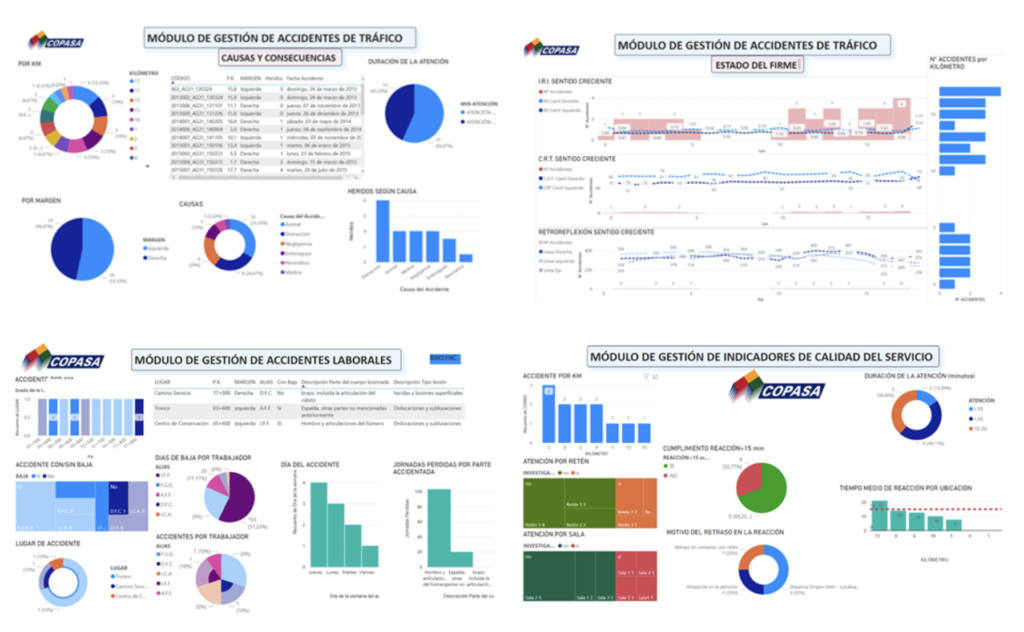
Information control panels for different modules
For cases that require it because of their complexity, virtual scenes are generated that allow access from different points of view and in a totally immersive way to the studied accident. The access to these scenes is done through links associated to the elements of the accident models or from the issues tables.
The use of virtual reality goggles improves the understanding of the causes and consequences of the accident, allowing a qualitative leap in the training of maintenance operators by interacting in the scene without the need for a real presence on the ground.

Immersion in Virtual Reality environments
The Results
The fundamental achievement of BIMSAFETY – ROADS was to outline an integrated tool for the management of safety and prevention-related information. This tool functions as a 3D repository and also allows the full potential of the data and visuals to be used for analysis from multiple perspectives. The objective is to be able to draw conclusions and take corrective actions or other types of decisions in near real time. In this sense, a major success of the implementation has been to establish applications that are truly tailored to the needs of road maintenance and operations contracts, both from the perspective of road safety and risk prevention and quality of service indicators. Finally, it should also be mentioned that for us, the project has effectively confirmed the usefulness of BIM in this field of road maintenance.
Pablo Jose Talavera Morato, BIM Manager of COPASA
Antonio Baamonde Roca, Road engineer of COPASA
Source: DAAG