Overview of ISO 19650
How did ISO 19650 evolve from PAS 1192-2?
ISO 19650 accreditation is an international standard that has its roots firmly planted in the older PAS 1192 (British standard) series. PAS 1192, or Publicly Available Specifications, initially defined the guidelines, codes of practices, and standards developed to fulfill the immediate information management needs of the UK building industry.
The transition from PAS 1192 to ISO 19650 signifies a global harmonization of best practices for information management using BIM (Building Information Modeling). This evolution aimed to provide a consistent, internationally recognized framework, enhancing collaboration and efficiency across global projects and asset lifecycles.
What is ISO 19650?
ISO 19650 is a series of BIM (Building Information Modeling) standards that comprehensively cover concepts and principles related to the organization and digitization of information management about buildings and civil engineering works, including security information.
This international standard defines the collaborative processes essential for effective information management throughout the entire lifecycle of a project or asset. The ISO 19650 standard aims to minimize wasteful activities and increase predictability in terms of cost and time for projects. It is crucial for achieving efficient digital information exchange and ensuring robust information management practices.

What are the core components and principles of ISO 19650?
The ISO 19650 standard is structured into several parts, each addressing specific aspects of information management and BIM (Building Information Modeling) within the built environment. These parts collectively define a robust framework for collaboration and information exchange.
ISO 19650-1: Concepts and Principles
This foundational part of the ISO 19650 standard defines the overarching concepts and principles for information management. It includes essential terms and definitions, outlining the definition of information requirements. Other critical aspects covered are the information delivery lifecycle, team structures, asset and project definitions, delivery planning, and how to manage collaborative production.
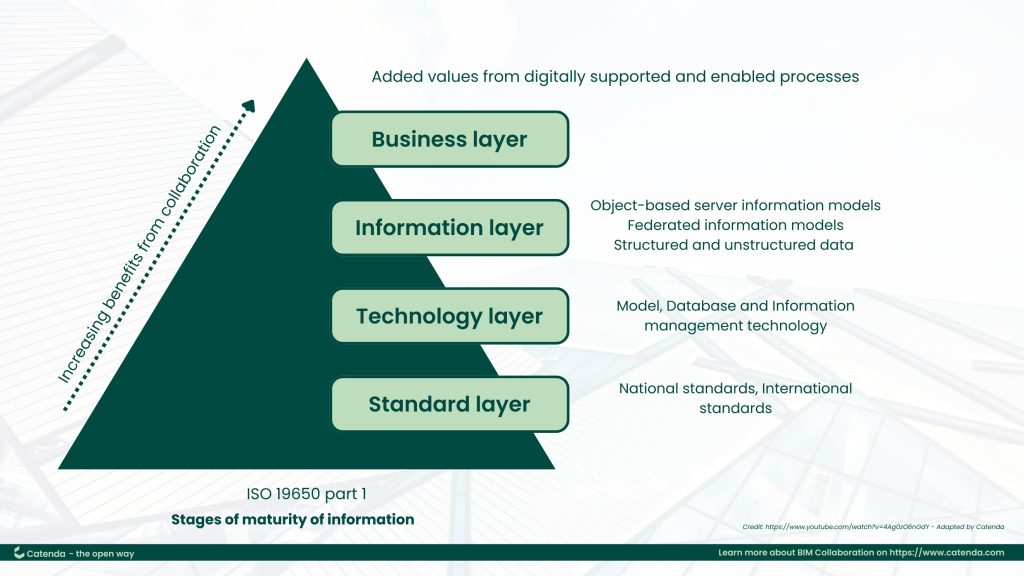
ISO 19650-1 also details Common Data Environment (CDE) solutions and workflows, which are central to effective information management. It includes sections for both the delivery phase, involving the Project Information Model (PIM), and the operational phase, with an Asset Information Model (AIM). This document also establishes stages of maturity for information management, emphasizing continuous improvement in digital collaboration.
ISO 19650-2: Delivery Phase of the Assets
ISO 19650-2 specifically outlines the information management during the delivery phase of assets. It details the management process and the requirements for a BIM (Building Information Modeling) Execution Plan (BEP), a crucial document for any project. This part ensures that information exchange is streamlined and consistent throughout the project delivery.
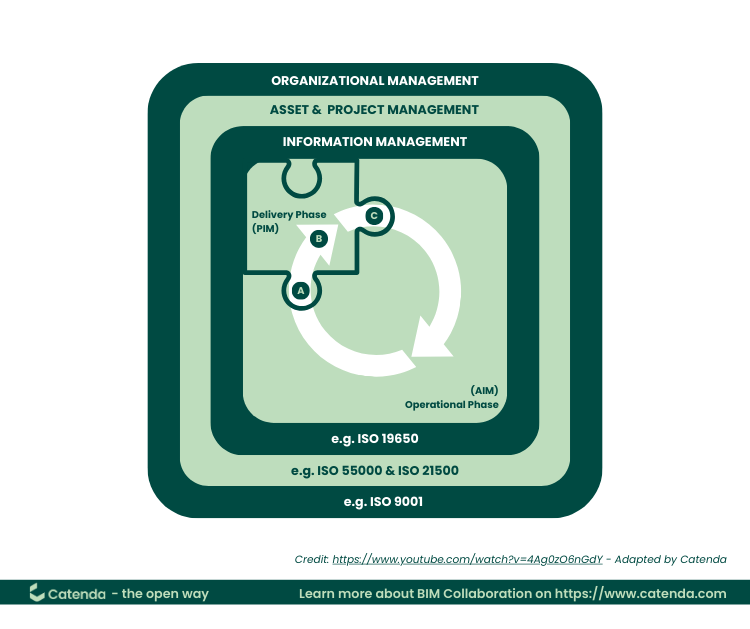
Scope of ISO 19650-2:
- AIM: Asset Information Model
- PIM: Project Information Model
- A: Start of delivery phase — transfer of relevant information from AIM to PIM
- B: Progressive development of the design intent model into the virtual construction model
- C: End of delivery phase — transfer of relevant information from PIM to AIM
ISO 19650-3: Operational Phase of the Assets
Focusing on the operational phase of assets, ISO 19650-3 provides guidelines for the Common Data Environment (CDE), BIM Execution Plan (BEP), asset information standards, production methods and procedures, and team delivery capacities and capabilities. This ensures effective information management even after the project’s completion.
ISO 19650-4: Information Exchange
ISO 19650-4 specifies the procedure and criteria regarding information exchange. It describes how to implement ISO 19650-1 principles for ISO 19650-2 and ISO 19650-3 stages. The measures and controls address specific Exchange Information Requirements (EIR), ensuring that digital information is exchanged efficiently and securely.
ISO 19650-5: Security-minded Information Management
ISO 19650-5 highlights the critical aspect of security in information management. It is related to the delivery and operational phases of assets when using BIM (Building Information Modeling). This document enables teams to minimize wasteful activities and increase predictability (i.e., cost and time) by ensuring the security of sensitive information.
Key Documents in the ISO 19650 Process: During the ISO 19650 process, several critical documents are needed to facilitate effective information management and collaboration:
- OIR – Organizational Information Requirements
- PIR – Project Information Requirements
- EIR – Exchange Information Requirements
- AIR – Asset Information Requirements
- BEP – BIM (Building Information Modeling) Execution Plan
- RM – Responsibility Matrix
- TIDP – Task Information Delivery Plans
- MIDP – Master Information Delivery Plan
- RACI – Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed (a matrix for defining roles and responsibilities)
What are the key benefits of ISO 19650 in construction, and why is it important?
The adoption of ISO 19650 in construction brings a multitude of benefits, making it an indispensable standard for modern projects. Its importance lies in fostering a more efficient, collaborative, and predictable built environment.
- ISO 19650 significantly enhances information management. By providing a structured approach to creating, managing, and exchanging digital information, it reduces data loss and ensures that all project participants work with the most current and accurate data. This streamlined information exchange is crucial for complex BIM (Building Information Modeling) projects.
- The standard promotes improved collaboration. Through the implementation of a Common Data Environment (CDE) and clear requirements for information exchange, all stakeholders can access and contribute to project information in a standardized manner. This reduces miscommunication, errors, and rework, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings throughout the asset lifecycle.
- ISO 19650 contributes to risk reduction. By standardizing processes and establishing clear requirements for information security and quality, it helps identify and mitigate potential issues early in the project lifecycle. This proactive approach minimizes costly delays and disputes.
- The ISO 19650 standard supports the overall digital transformation of the construction industry. It enables organizations to leverage BIM (Building Information Modeling) to its full potential, leading to more sustainable, resilient, and high-performing assets. Achieving compliance with this standard demonstrates a commitment to best practices and positions organizations competitively in the global market.
Who are the key stakeholders in ISO 19650 compliance, and what are their roles?
Achieving ISO 19650 compliance requires a clear understanding of the various stakeholders involved and their specific roles and responsibilities within the information management process. Collaboration among these parties is paramount for successful project delivery and asset management.
Identifying Key Stakeholders
In the ISO 19650 framework, key stakeholders are typically categorized based on their involvement in the information management process. These include:
- Appointing Party: This is the entity that initiates a project and defines the information requirements. They are responsible for setting the overall strategic objectives and ensuring that the ISO 19650 standard is adopted.
- Lead Appointed Party: This party is appointed by the Appointing Party to manage the overall information management process for a project. They are responsible for coordinating information exchange and ensuring compliance with the EIR (Exchange Information Requirements).
- Appointed Parties: These are the various organizations or individuals (e.g., designers, contractors, specialists) appointed by the Lead Appointed Party to deliver specific information or services related to the project.
- Information Managers: These individuals or teams are responsible for the day-to-day management of information within the Common Data Environment (CDE), ensuring data quality, security, and adherence to ISO 19650 standards.
Roles and Responsibilities
Each stakeholder has distinct roles and responsibilities crucial for effective information management and BIM (Building Information Modeling) implementation:
- Appointing Party: Defines Organizational Information Requirements (OIR), Project Information Requirements (PIR), and Asset Information Requirements (AIR). They establish the Exchange Information Requirements (EIR) and ensure contractual requirements align with ISO 19650.
- Lead Appointed Party: Develops the BIM (Building Information Modeling) Execution Plan (BEP), manages the Common Data Environment (CDE), coordinates information exchange between appointed parties, and ensures the quality and security of information. They are central to facilitating collaboration.
- Appointed Parties: Produce information in accordance with the BEP and EIR, contribute to the Common Data Environment (CDE), and adhere to the specified information management procedures. They are responsible for the accuracy and completeness of their deliverables.
- Information Managers: Oversee the Common Data Environment (CDE) workflow, manage access permissions, ensure auditability of information, and facilitate the seamless flow of digital information throughout the project lifecycle. They ensure the standard’s principles are upheld.
ISO 19650 and Common Data Environment (CDE)
The definition and importance of CDE in ISO 19650
The Common Data Environment (CDE), as defined by ISO 19650, is the agreed source of information for a given project or asset, responsible for collecting, managing, and disseminating each information container through a managed process. The CDE serves as a cloud-based data platform to store construction project information. It provides project participants access to this information based on their requirements, contractual obligations, and authorization level. This centralization of data contributes to improved collaboration, enhanced information management, and increased efficiency, thus playing an instrumental role in the effective BIM management in construction.
What is the role of a CDE in achieving compliance with ISO 19650?
The Common Data Environment (CDE) plays a pivotal role in achieving compliance with ISO 19650. It acts as a centralized repository for collecting, managing, and disseminating all graphical and non-graphical information throughout a project’s lifecycle.
A CDE platform should offer functionalities such as:
- Version Control: To manage changes to information containers and maintain an audit trail.
- Access Control: To ensure that only authorized personnel can view, modify, or approve information, adhering to security requirements.
- Workflow Management: To guide information through various stages (e.g., work in progress, shared, published, archived) as defined by ISO 19650.
- Clash Detection and Model Coordination: While not strictly a CDE feature, integration with BIM (Building Information Modeling) authoring and coordination software is essential for identifying and resolving design conflicts early in the project lifecycle.
- Data Validation: Tools that can check information against predefined requirements and standards to ensure quality and consistency.
To achieve compliance, contractors must establish comprehensive protocols within the CDE, including user access and permissions management. This ensures that data is shared, stored, and managed effectively, thereby aligning with the ISO 19650’s emphasis on standardized processes and guidelines for efficient information management.
Moreover, understanding the ISO 19650 standards is crucial before implementing them. This includes understanding the functional characteristics of a CDE as defined by ISO 19650, such as its role as the “agreed source of information for any given project or asset”. By thoroughly understanding these standards, BIM teams can ensure proper utilization of the CDE, thereby facilitating ISO 19650 compliance.
How to manage a CDE under ISO 19650 standards?
Managing the Common Data Environment (CDE) under ISO 19650 standards entails establishing comprehensive protocols to ensure effective information management.
A key aspect of this is access and permissions management. This means setting rules for who can view, modify, or delete information within the CDE.
Another crucial element is the auditability of logs, which document how data is manipulated and shared. Transparency in these processes is vital.
Finally, a CDE must be supported by a combination of technical solutions and process workflows, as suggested by ISO 19650. It is not only about the software but also the processes that enable efficient information management.
What are the practical steps to achieve ISO 19650 compliance?
Achieving ISO 19650 compliance is a systematic process that requires careful planning, implementation, and continuous monitoring. It involves integrating the standard’s principles into an organization’s existing workflows and adopting a digital-first approach to information management.
The journey to ISO 19650 compliance begins with a thorough understanding of the standard’s requirements and a commitment from leadership.
- Awareness and Training: Educate key personnel on the principles of ISO 19650 and BIM (Building Information Modeling). Training should cover the various parts of the standard, the role of the Common Data Environment (CDE), and the importance of structured information management.
- Gap Analysis: Conduct an assessment of current information management practices against the ISO 19650 requirements. Identify areas where existing processes, technologies, and competencies fall short. This analysis will form the basis of your implementation plan.
- Define Information Requirements: Clearly articulate your Organizational Information Requirements (OIR), Project Information Requirements (PIR), Asset Information Requirements (AIR), and Exchange Information Requirements (EIR). These documents are fundamental to guiding information production and exchange.
- Implement a Common Data Environment (CDE): Establish a robust Common Data Environment (CDE) as the single source of truth for all project and assetinformation. This platform is critical for enabling collaboration and managing the flow of digital data.
- Develop a BIM Execution Plan (BEP): Create a detailed BIM Execution Plan that outlines how information will be produced, exchanged, and managed throughout the project. This document is essential for guiding the digital workflow.
- Continuous Improvement: ISO 19650 is not a one-time achievement but an ongoing commitment. Regularly review and refine your information management processes, adapting to new technologies and lessons learned from past projects to maintain compliance and optimize efficiency.




